Plastic Heat Stake Solutions
Heat staking works well with many difficult thermoplastics including the glass-filled plastics used in medical devices, automotive, appliances, telecom, electronics and consumer products.
The heat staking process can be used in a variety of applications including:
- Panel assemblies
- Joining printed circuit boards to plastic housing
- Joining electronic components to plastic housing
- Medical device assembly
The most common resins used in heat staking are:
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Nylons (GFN or Nylon 6/6)
- Ultem (GFN or Nylon 6/6)
If you are designing a part that will be joined to another, contact Ferriot to determine if heat staking is the right solution for your project.
Learn more:
- 12 Steps for Choosing the Right Injection Molding Resin for Your Part
- Case Study: Finishing Operations for Fluid-Injection Pumps
- Case Study: Finishing Operations for Wheelchair Components
FAQ
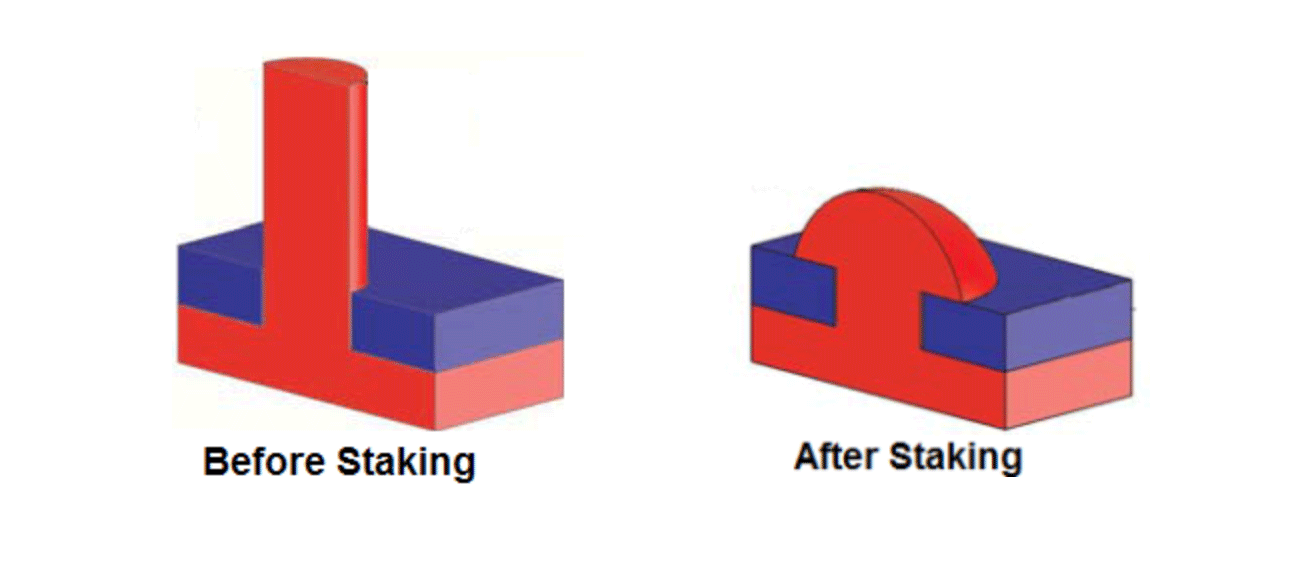
What is heat staking?
Heat staking is a process used in plastic assembly where at least one of the parts is made from thermoplastic. It is commonly used to join metal parts to plastics or to join two dissimilar plastic components. The process involves the application of heat and pressure to soften a specific area of the plastic, which is then remolded into a new shape or profile that forms over or around the connecting part. Once cooled, the plastic’s strength holds the mating part in place, creating a permanent assembly without the need for additional fasteners or hardware.
Workbook Resin Selection
Ensuring that an injection molded part lives up to this potential depends in large part on choosing the best resin. This workbook details different part characteristics and how they influence your resin choice.
View the WorkbookHow can we help?
Ferriot’s experienced engineers are here to guide you through every critical step in your injection molding journey, from concept to completion.